What Is Venture Capital (VC)Funding?
Venture Capital (VC) funding is an investment route through which investors provide capital to high-potential growth stage startups in exchange for equity in the company. Venture capital firms also provide expertise and mentorship to their portfolio companies.
A VC firm manages money from wealthy individuals, insurance companies, pension funds, foundations and corporate pension funds who pool their money to create a fund, aka VC fund. These funds are governed by VC firms that take all investment decisions.
Typically, a VC firm raises capital for its funds from limited partners (LPs), with general partners (GPs) also making a capital contribution in some cases. The primary responsibility of a general partner is to allocate and manage the funds raised from limited partners.
VC fund managers receive management fees and carry interest (a share of the profit made by the VC firm). About 20% of the profits made by the fund go to the VC firm, which manages the private equity fund. The remaining profits are distributed among limited partners who invested in the fund. The VC firm typically receives an additional 2% fee for its services.
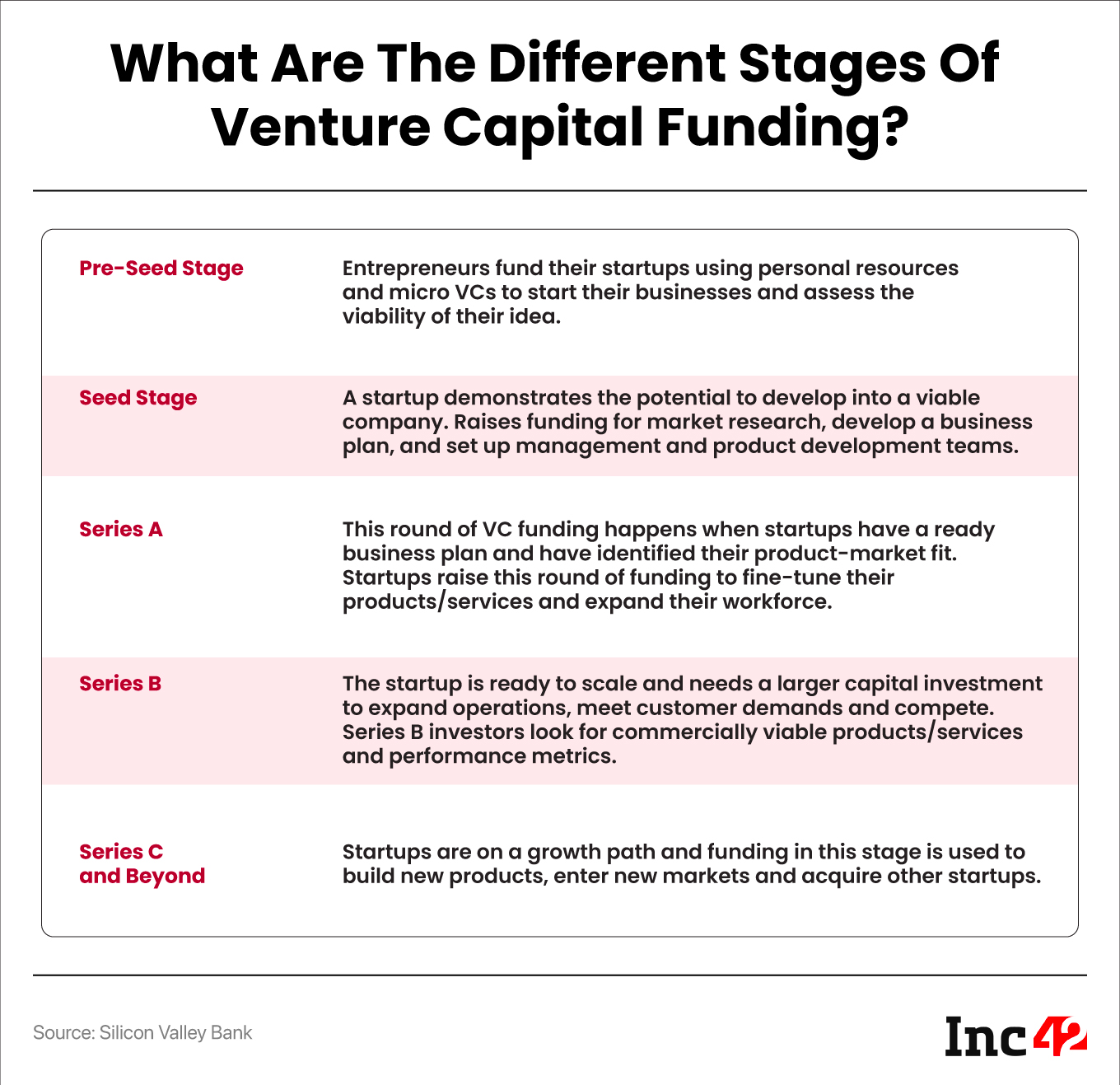
What Are The Benefits Of Venture Capital (VC) Funding?
- Venture capital provides startups with the necessary funds to scale their operations rapidly, hire talent, expand their market presence and develop innovative products or services.
- VC funding allows startups to focus on growth without any financial obligations like traditional bank loans or debt financing.
- VCs bring in their experience and expertise to assist startups with strategic planning, market research, and legal support, mitigating the chances of failure.
- VC firms often provide long-term support to startups by participating in multiple funding rounds and acting as anchor investors, attracting other investors and providing stability to the business.
- Startups can leverage VC networks to connect with new clients, partners and employees, opening doors to new opportunities for growth and collaboration.
- VCs bring valuable mentorship to startups, helping them make informed decisions, overcome challenges, and optimise their operations.
- Venture capital firms facilitate collaboration among their portfolio companies, fostering synergies and mutual growth opportunities. Startups can benefit from partnerships within the VC’s network.
- A VC can enhance a startup’s credibility and visibility in the market and attract potential clients, partners, and investors.
What Are The Risks Associated With Venture Capital (VC) Funding?
- To seek VC funding, startups often have to give up a substantial portion of their equity in exchange for funding. This dilutes their ownership and may lead to potential conflicts with investors’ short-term goals.
- A startup may lose substantial control over its company as investors may demand significant equity in the company.
- Raising venture capital is a time-consuming process, involving multiple rounds of negotiations, due diligence and investor pitches.
- Investors may seek a high level of expertise and experience in the startup’s team, making it challenging for first-time entrepreneurs to get investments.
- VCs may prioritise short-term gains over long-term growth, further conflicting with the interest of the startup founders looking to grow sustainably.
- Startups may face competition from portfolio startups when seeking VC funding as investors have multiple opportunities to choose from.
How Do Venture Capital (VC) Firms Conduct Due Diligence?
Initial Screening: Startup evaluation for due diligence starts with an initial screening to determine its viability. It usually involves the preliminary review of the startup’s business plan, market opportunity, and management team. It helps the VC firm filter out startups that are not aligned with the firm’s criteria or lack growth potential. Once a startup is selected, the VC firm proceeds to the subsequent stages of the due diligence process for deeper evaluation.
Market Research: Investment analysts investigate the market size, product-market fit (PMF) competition, trends and growth potential. The analysts assess startups’ target market share and demand for their products. They also identify the risks and potential that come with these startups.
Financial Analysis: They evaluate startups by examining their balance sheets, cash flows, revenues, expenses, and projections. They also study their capital structure and customer acquisition model and verify transparent accounting policies and practices.
Legal Review: Analysts assess legal and regulatory compliance status to understand if the startup under review is under any legal or contractual liability that could potentially impact investments. They further review governance structure, contractual obligations, and intellectual property.
Technology Assessment: Investors also investigate the quality, capabilities, limitations and scalability of startups’ technology.
Customer Validation: To validate the quality, uniqueness, and market appeal of startups’ offerings, VCs rely on customer feedback to ascertain if the founders have found the right product-market fit.
Management Evaluation And Reputation Check: While assessing startups, investors evaluate teams’ experience, expertise and skills. Investors also seek feedback from peers about working with the founder. This helps them understand the founders’ ability to lead the company through growth and market changes.
Once the due diligence report is ready, a VC analyst compiles all the evaluations of a report to present it to the investment committee with a recommendation. Conducting reverse due diligence on the VC firm’s background and reputation is also important for startup founders.
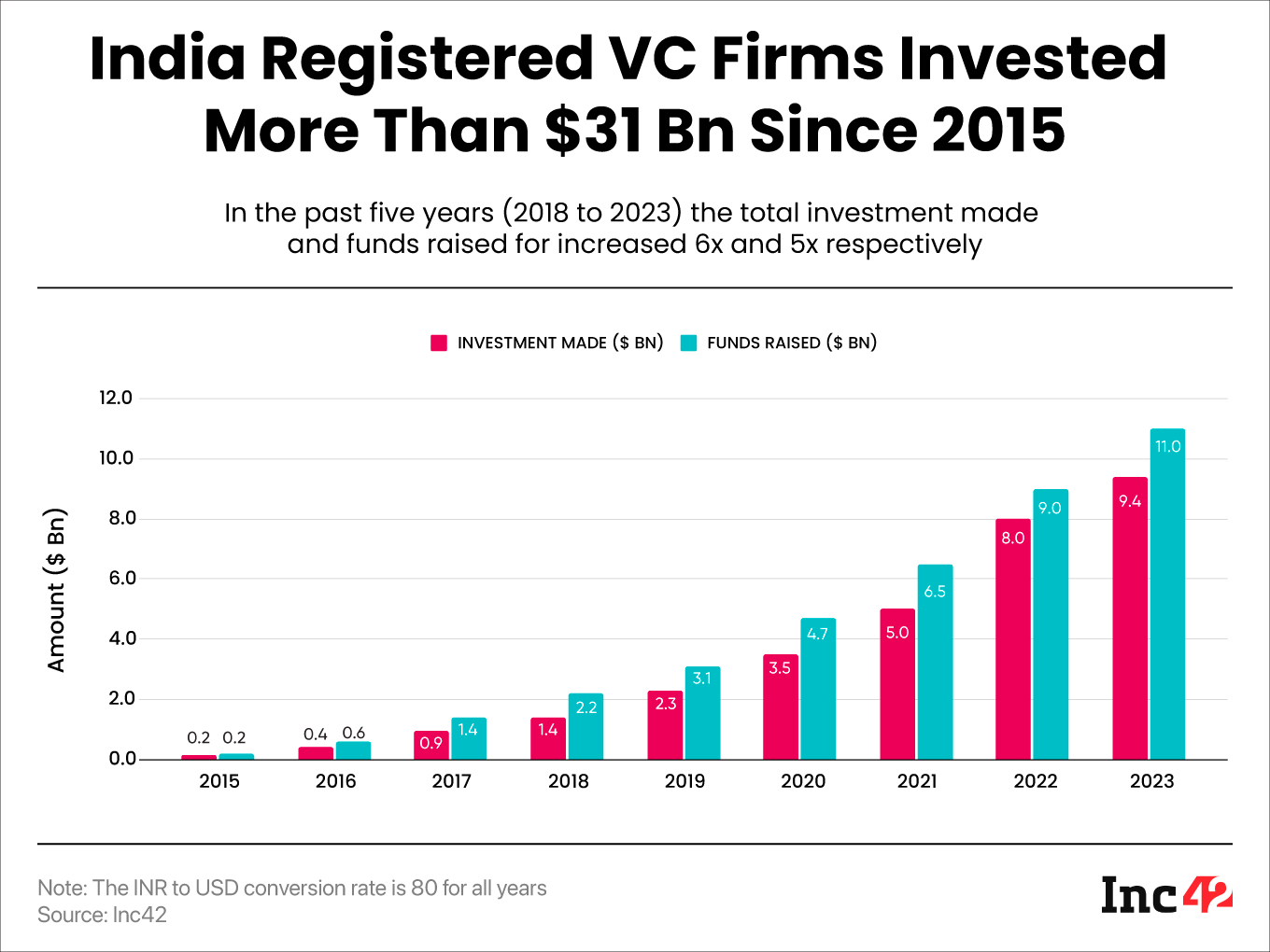
What Is The Venture Capital (VC) Funding Scenario In India?
How To Approach Venture Capital (VC) Firms To Raise Funding?
According to experts, before reaching out to any VC firm to raise funding, entrepreneurs must thoroughly research the market and choose active investors within the respective sector.
Once the investor list has been narrowed down, startups must conduct background research on each investor and their VC firms. Founders must ensure that these investors have invested in their respective sectors before approaching them.
Once the research is conducted, potential founders can reach out to VC firms through networking events or online platforms like LinkedIn or directly through their websites.
Once the founders are connected to the VC firms and a meeting is arranged, they would be required to prepare a crisp pitch explaining the business plan, create an impact, and impress the investor in one meeting.
How To Pitch For Venture Capital (VC) Funding?
Following the MVP stage, founders can seek venture capital by preparing a to-the-point pitch to get venture capitalists to invest. Here are some salient features that a pitch should include:
- It should focus on the solution or the value proposition that the startup’s product/service is offering and relevant data to show the clear need for it in the market.
- Founders must highlight the differentiating value of the product/service that can stand out in a competitive market, and your goals and objectives should clearly come out in the pitch.
- Clearly explain the long-term vision and exit strategy to attract investors looking for profitability during liquidity events as an ROI.
- Define the startup’s survival strategy for the next few years. It should include a runway, a comprehensive business plan with product/service details, an overview of the target market, competitor analysis and financial forecasting.
- The pitch deck must also include details of establishing a team and a business execution plan.
- All key points should be shown to investors through accurate and compelling statistics, including marketing and sales strategies, to demonstrate growth potential.
- The pitch should show proof of concept that the startup is scalable.
What Exits Do Venture Capital (VCs) Take?
Secondary Market Sale: VCs can exit their investments by selling their holdings to new investors in the private equity secondary market, especially during later funding rounds. This step comes before an IPO.
Mergers & Acquisition: In this strategy the portfolio company gets acquired by another firm, either by a strategic buyer interested in the growth and technology or a financial buyer.
Initial Public Offering (IPO): If the company performs well and goes public, venture capitalists can sell their shareholdings in the open marketplace after the IPO.








