What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software system that helps businesses manage and integrate all their core activities. Imagine it as a central hub for all company’s data and processes like finance, accounting, inventory, and human resources.
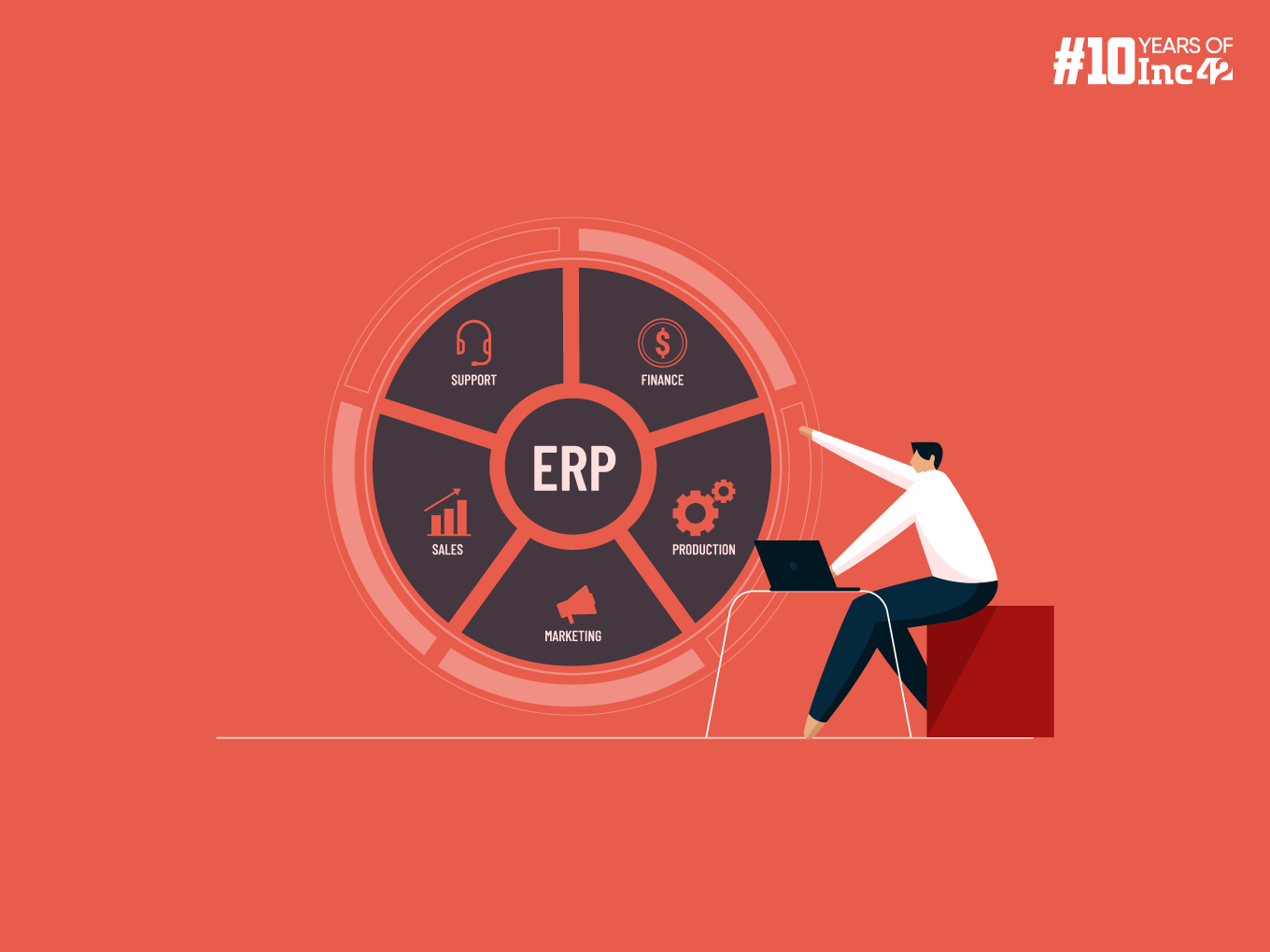
What Are The Core Functionalities Of An ERP System?
An ERP system boasts a wide range of functionalities, but at its core, it focusses on integrating various departments and streamlining processes. Some of its key functionalities are as follows:
- Financial Management: ERP systems manage financial transactions, accounting processes and reporting. This includes accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, and financial consolidation.
- Inventory Management: ERP keeps track of inventory levels, orders and fulfilment. It helps businesses optimise stock levels, avoid stockouts, and ensure they have the required materials.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP integrates CRM functionality, which helps businesses manage interactions with customers and sales leads. This includes tracking customer contact information, sales opportunities, and service requests.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): The HRM component of ERP handles HR processes like payroll, recruitment, and benefits. It ensures employees are paid accurately and on time.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): ERP tracks and manages the flow of goods and materials throughout the supply chain. This includes purchasing, inventory management, warehousing and transportation.
How Does An ERP System Benefit A Business?
Businesses can reap a multitude of benefits from implementing an ERP system. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency & Productivity: ERP automates manual tasks and streamlines workflows across departments, freeing up employees’ time and reducing errors.
- Improved Visibility & Data Accuracy: ERP creates a single source of truth for all your business data. This provides everyone in the company access to real-time, accurate information, improving visibility into operations.
- Enhanced Collaboration & Communication: By sharing a central platform, departments can collaborate more effectively and communicate seamlessly. This fosters transparency and breaks down information silos.
- Better Scalability & Flexibility: ERP systems are designed to grow with the business. As a company expands, it can add new modules or features to meet its needs.
What Are The Key Considerations For A Company When Implementing An ERP System?
A company must carefully consider several factors to ensure a successful ERP system implementation. The following are some key considerations:
- Business Needs Assessment: The first step is understanding the company’s current business processes, pain points, and desired improvements, which will guide the selection of the most suitable ERP system and functionalities.
- Data Migration And Cleansing: ERP implementation often involves migrating data from existing systems. This process requires careful planning and execution to ensure data accuracy and completeness in the new system.
- Change Management And User Adoption: Implementing a new ERP system can significantly impact company workflows. A successful implementation requires a well-defined change management strategy to address employee concerns and ensure user adoption.
- Integration With Existing Systems: Most companies have software systems for specific functions. The chosen ERP system should integrate seamlessly with these systems to avoid data silos and ensure a unified flow of information.
How Does An ERP System Ensure Data Integrity And Consistency Across Different Departments?
An ERP system utilises several tools and strategies to ensure data integrity and consistency across different departments:
- Centralised Database: ERP systems function with a single, unified database that stores all business information. This eliminates the issue of data silos and discrepancies that can arise when departments use separate software programs.
- Data Validation Rules: ERP systems often have built-in data validation rules that act as gatekeepers for information entry. By enforcing these rules, the system helps prevent errors and inconsistencies in data entry.
- Standardisation: ERP systems promote data consistency by enforcing standardised formats and definitions for data elements. Standardisation ensures everyone uses the same terminology and data formats.
- Data Change Tracking & Auditing: Many ERP systems track changes made to data, creating an audit trail. This allows companies to see who made changes when they were made, and the previous value of the data. This audit trail is crucial to maintain data integrity and accountability.
- Data Cleansing & Integration: ERP implementations often involve migrating data from existing systems. A crucial step is data cleansing, where the data is reviewed and corrected to ensure accuracy before migration to the central ERP database.
How Does An ERP System Integrate With Existing Business Applications
ERP systems can integrate with existing business applications to create a more unified and streamlined business ecosystem in many ways:
- Pre-Built Connectors & APIs: Modern ERP systems often have pre-built connectors and APIs that connect commonly used business applications. These pre-built integrations allow seamless data exchange between the ERP and other applications.
- Custom Integration: For applications that don’t have pre-built connectors, companies can leverage third-party integration tools.
- Point-To-Point Integration: In some cases, companies may opt for point-to-point integration, where a custom code is developed to connect the ERP system directly to a specific application.
- Cloud-Based Integration Platforms: Cloud-based ERP systems often integrate well with other cloud-based applications through cloud integration platforms (iPaaS).