What Is Direct To Consumer (D2C)?
The D2C model has gained immense popularity over the last few years, offering businesses a means to eliminate intermediaries, gain a closer understanding of market dynamics and directly sell their products to consumers.
D2C brands leverage their own websites in order to create strong consumer relations, gain more control over the customer experience and ensure lasting customer retention.
In India, there are more than 50K digital-first brands today.
What Are The Benefits Of D2C Over Traditional Retail Channels?
Following are some of the advantages of going D2C:
Direct Interactions: Traditional retailers generally rely on market research and surveys to understand consumer sentiment and preferences. However, the D2C model lets businesses engage directly with customers at every stage, helping them gain valuable insights to enhance the shopping experience and subsequently increase market share.
Reduced Time To Market: A consumer packaged goods (CPG) brand will need 18-36 months from inception for its products to reach the stores due to multiple stakeholders and approvals involved in the process. However, for a D2C brand, it is as easy as setting an Instagram account and listing one’s WhatsApp business number to start the business. Starting small allows D2C brands to devise a quick growth plan before going full throttle.
Creating A Brand Identity: In traditional retail, a brand’s control is often limited to its packaging and outbound marketing efforts. Consequently, this can lead to the brand getting lost amid a sea of options, especially when it’s a new and emerging one. The D2C route allows brands greater control over product packaging, marketing messages, managing deliveries and curating post-purchase experience.
Multiple Integrated Sales Channel: Besides leveraging their own websites, D2C brands can list themselves on various marketplaces to gain more visibility and acquire a larger customer base. In addition, enablers, including martech platforms and website builders, equip online brands with customer and business insights that help them improve their market performance.
What Is The State Of D2C Brands In India Today?
India’s D2C market opportunity is growing at a fast clip. According to Inc42’s estimates, D2C brands raised more than $925 Mn funding in H1 2023 — out of this, Lenskart bagged a whopping $700 Mn in funding from marquee investors like AIDA and ChrysCapital.
The D2C market is expected to account for 75% or $300 Bn of ecommerce’ $400 Bn market opportunity by 2030, making it the largest and fastest-growing segment within the ecommerce landscape.
Several factors are responsible for the hyper-growth trajectory of the D2C market. Today, India has the third-largest online shopping base in the world, after the US and China, giving impetus to the growing D2C market. The rising internet penetration has also empowered shoppers beyond the metros, making online retail even more accessible.
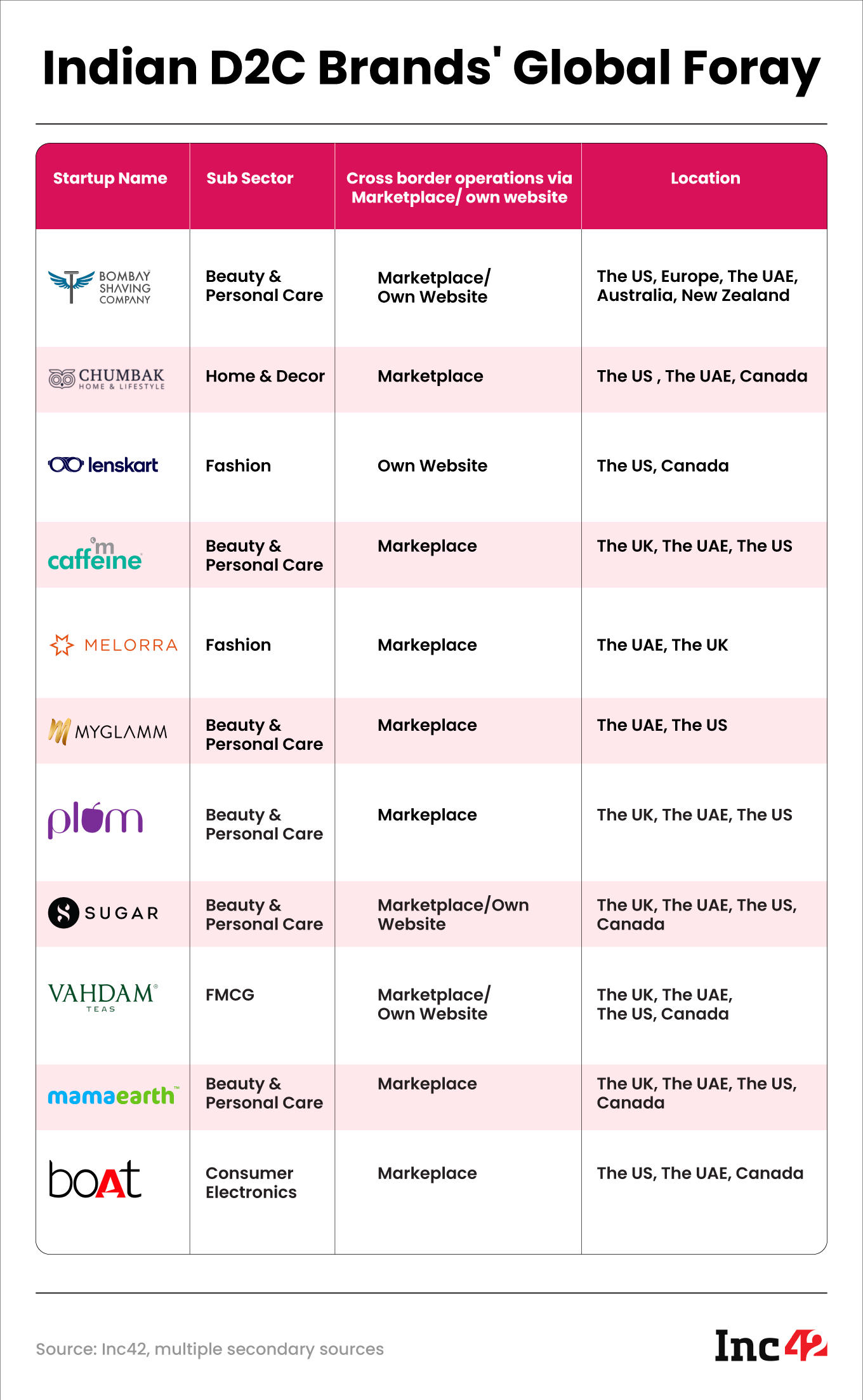
As many D2C brands have already made a dent in the Indian market, they are now dipping their toes into the cross-border opportunity which is being considered as the next big growth driver for India’s D2C brands.
When Should D2C Brands Take The Offline Route?
Over the years, brands have evolved their sales strategy, shifting from pure-play D2C (read leveraging their own websites) to omnichannel giants with a presence across websites, marketplaces and offline retail stores. SUGAR Cosmetics, Mamaearth and Lenskart are some of the prominent D2C brands that have perfected the omnichannel approach.
However, brands should consider the following parameters before taking the offline plunge:
- Shelf Life: Offline retail works better for products with a longer shelf life. Offline retail can make the distribution process longer. Hence, it may not be beneficial for fresh foods and perishable goods.
- Understanding The Category: The share of ecommerce in some of the sectors such as electronics, apparel, and beauty is already at 30-40%, allowing D2C startups in these segments to achieve significant growth without the need for a physical presence. However, D2C brands operating in categories with lower ecommerce penetration should first attain their product-market fit, establish brand loyalty and then expand offline.
What Legal & Regulatory Considerations Do D2C Startups Need To Be Aware Of?
Following are some of the important legal and regulatory considerations for D2C startups:
Register Your Startup: To start a business in India, entrepreneurs must register the entity with the Registrar of Companies (RoC). The Companies Act 2013 and the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act govern registrations.
Obtain Necessary Licences: Startups may be required to obtain specific licences for specific businesses. Such licences are issued by several regulatory bodies including municipal corporations, the Food Safety & Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), among others.
Legal Agreements: Before starting a business, some legal arrangements may be required with vendors, suppliers, customers and other stakeholders, such as vendor, service and employment agreements. Such agreements limit the liability and obligations of the business.
Tax Regulations: Besides obtaining a PAN and a TAN card, startups are required to register for Goods & Services Tax (GST) if their turnover is more than INR 20 Lakh.
Protecting Intellectual Property (IP): IPs can be protected under patents, trademarks and copyrights. The Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks grants these protections after verifying the application.
Data Protection: It is important to create and foster consumer trust if a brand aims to corner long term success. Data protection is crucial in this regard as consumers can become vary of a brand if their privacy is threatened or compromised. Given the scenario, D2C brands must implement data protection measures and comply with data protection regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA).
What Are The Key Metrics That D2C Brands Should Track To Measure Their Success & Growth?
A few important metrics to measure growth are:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Being aware of how much expense is incurred on a customer allows brands to gauge the efficiency of marketing and advertising strategies, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding budget allocation.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Understanding the CLTV is crucial as it enables brands to calculate the appropriate budget for customer acquisition and retention efforts. It also helps identify valuable customers who are worth investing in for sustained and long-term relationships.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): MRR is a predictable metric of the recurring revenue of a business. It helps brands forecast their revenues and make informed decisions about the cash flows and budgeting.








